Armenians: Difference between revisions - Wikipedia
 Article Images
Article Images
Tags: Visual edit Mobile edit Mobile web edit Advanced mobile edit
Line 62:
| pop19 = 40,000<ref>{{cite web|title=Բելգիայում հայերի ներկայությունն անփոխարինելի է. Բրյուսելի քաղաքապետ|url=https://www.1lurer.am/hy/2020/02/22/|work=1lurer|date=22 February 2020|access-date=17 October 2020}}{{Dead link|date=September 2023 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref>
| region20 = Spain
| pop20 = 40,000<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://spain.mfa.am/en/community-overview/|title=Armenian Diaspora in Spain|website=Embassy of the Republic of Armenia to Spain|publisher=Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Armenia|access-date=7 April 2016|archive-date=31 March 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160331221826/http://spain.mfa.am/en/community-overview/|url-status=dead}}</ref>
| region21 = Bulgaria
| pop21 = 30,000<ref>{{cite web |title=Bulgaria |url=http://diaspora.gov.am/en/pages/54/bulgaria |website=Office of the High Commissioner for Diaspora Affairs |access-date=2023-06-20 |archive-date=21 June 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230621022151/http://diaspora.gov.am/en/pages/54/bulgaria |url-status=live }}</ref>
Line 87:
}}
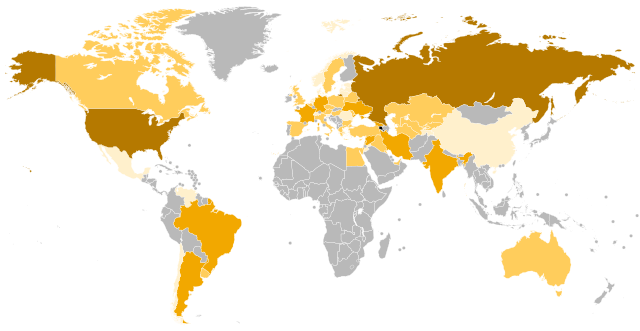
'''Armenians''' ({{lang-hy|հայեր|hayer}}, {{IPA-hy|hɑˈjɛɾ|}}) are an [[ethnic group]] and nation native to the [[Armenian highlands]] of West Asia.<ref name="Hewsen">[[Robert Hewsen|Hewsen, Robert H.]] "The Geography of Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: From Antiquity to the Fourteenth Century''. [[Richard G. Hovannisian]] (ed.) New York: St. Martin's Press, 1997, pp. 1–17</ref><ref name="loc.gov">{{cite web |author=<!--Staff writer(s); no by-line.--> |date=2020 |title=Armenian Rarities Collection |url=https://www.loc.gov/collections/armenian-rarities/about-this-collection/ |url-status=live |website=www.loc.gov |location=Washington, D.C. |publisher=[[Library of Congress]] |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230307021523/https://www.loc.gov/collections/armenian-rarities/about-this-collection/ |archive-date=7 March 2023 |access-date=27 March 2023 |quote=The lands of the Armenians were for millennia located in [[Eastern Anatolia]], on the [[Armenian Highlands]], and into the [[Caucasus Mountains|Caucasus Mountain range]]. First mentioned almost contemporaneously by a Greek and Persian source in the 6th century BC, modern DNA studies have shown that [[Origin of the Armenians|the people themselves had already been in place for many millennia]]. Those people the world know as Armenians call themselves ''Hay'' and [[Armenia|their country]] ''Hayots' ashkharh''–the land of the Armenians, today known as Hayastan. Their language, ''[[Armenian language|Hayeren]]'' (Armenian) constitutes a separate and unique branch of the [[Indo-European languages|Indo-European linguistic family tree]]. A spoken language until [[Christianization of Armenia|Christianity became the state religion]] in 314 AD, [[Armenian alphabet|a unique alphabet was created]] for it in 407, both for the propagation of the new faith and to avoid assimilation into the [[Persian literature|Persian literary world]].}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=Armenia: Ancient and premodern Armenia |website=[[Encyclopædia Britannica Online]] |url=https://www.britannica.com/place/Armenia/Administration-and-social-conditions#ref481320 |publisher=[[Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.]] |access-date=17 July 2018 |quote=The Armenians, an Indo-European people, first appear in history shortly after the end of the 7th century BCE[, d]riving some of the ancient population to the east of Mount Ararat [...] |archive-date=26 April 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190426135102/https://www.britannica.com/place/Armenia/Administration-and-social-conditions#ref481320 |url-status=live }}</ref> Armenians constitute the main population of the [[Armenia|Republic of Armenia]] and constituted the main population of the breakaway [[Republic of Artsakh]] until the [[2023 Azerbaijani offensive in Nagorno-Karabakh]] and the subsequent [[flight of Nagorno-Karabakh Armenians]].<ref>{{Cite news |last=Press |first=Associated |date=2023-09-30 |title=Almost all ethnic Armenians have left Nagorno-Karabakh |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2023/sep/30/almost-all-ethnic-armenians-have-left-nagorno-karabakh-azerbaijan |access-date=2024-03-04 |work=The Guardian |language=en-GB |issn=0261-3077}}</ref> There is a wide-ranging [[Armenian diaspora|diaspora]] of around five million people of full or partial Armenian ancestry living outside modern Armenia. The largest Armenian populations today exist in [[Armenians in Russia|Russia]], the [[Armenian American|United States]], [[Armenians in France|France]], [[Armenians in Georgia|Georgia]], [[Armenians in Iran|Iran]], [[Armenians in Germany|Germany]], [[Armenians in Ukraine|Ukraine]], [[Armenians in Lebanon|Lebanon]], [[Armenians in Brazil|Brazil]], [[Armenians in Argentina|Argentina]], [[Armenians in Syria|Syria]], and [[Turkey]]. The present-day [[Armenian diaspora]] was formed mainly as a result of the [[Armenian genocide]] with the exceptions of Iran, [[Post-Soviet states|former Soviet states]], and parts of the [[Levant]].<ref name="Hovannisian">[[Richard G. Hovannisian]], ''The Armenian people from ancient to modern times: the fifteenth century to the twentieth century'', Volume 2, p. 421, Palgrave Macmillan, 1997.</ref>
[[Armenian language|Armenian]] is an [[Indo-European languages|Indo-European language]].<ref name="loc.gov"/><ref>{{Cite web | url=https://www.britannica.com/topic/Armenian-people | title=Armenian (people) | Description, Culture, History, & Facts | access-date=5 September 2018 | archive-date=26 April 2019 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190426130529/https://www.britannica.com/topic/Armenian-people | url-status=live }}</ref> It has two [[Mutual intelligibility|mutually intelligible]] spoken and written forms: [[Eastern Armenian]], today spoken mainly in Armenia, Artsakh, [[Iran]], and the former Soviet republics; and [[Western Armenian]], used in the historical [[Western Armenia]] and, after the Armenian genocide, primarily in the Armenian diasporan communities. The unique [[Armenian alphabet]] was invented in 405 AD by [[Mesrop Mashtots]].