Creatine: Difference between revisions - Wikipedia
 Article Images
Article Images
Content deleted Content added
Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
|||
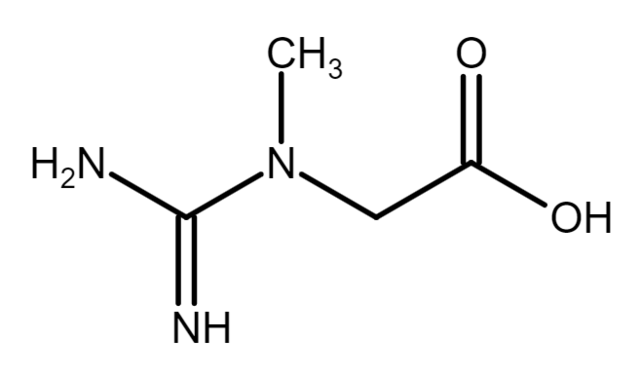
Line 128: ==== Loading phase ==== [[File:Muscle_Total_Creatine_Stores.png|alt=|thumb|485x485px]] An approximation of 0. This elevation in muscle creatine storage has been correlated with ergogenic benefits discussed in the research section. However, higher doses for longer periods of time are being studied to offset creatine synthesis deficiencies and mitigating diseases.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Hanna-El-Daher L, Braissant O | title = Creatine synthesis and exchanges between brain cells: What can be learned from human creatine deficiencies and various experimental models? | journal = Amino Acids | volume = 48 | issue = 8 | pages = 1877–95 | date = August 2016 | pmid = 26861125 | doi = 10.1007/s00726-016-2189-0 | s2cid = 3675631 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Bender A, Klopstock T | title = Creatine for neuroprotection in neurodegenerative disease: end of story? | journal = Amino Acids | volume = 48 | issue = 8 | pages = 1929–40 | date = August 2016 | pmid = 26748651 | doi = 10.1007/s00726-015-2165-0 | s2cid = 2349130 }}</ref><ref name="creatinedefects" /> | |||