Kanhaiya Misl: Difference between revisions - Wikipedia
 Article Images
Article Images
Content deleted Content added
Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit Advanced mobile edit |
m |
||
| (38 intermediate revisions by 16 users not shown) | |||
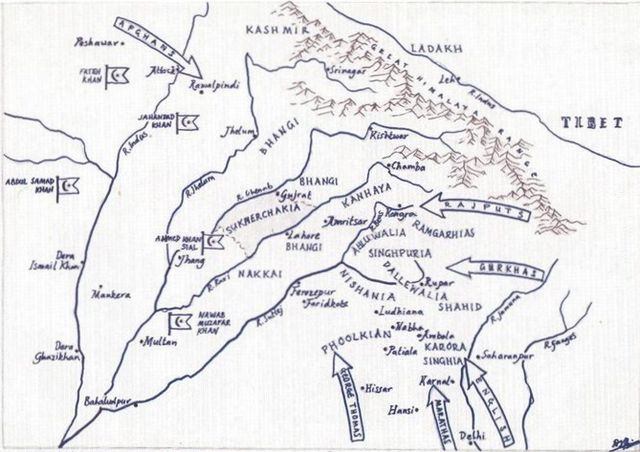
Line 2: {{Use dmy dates|date=January 2018}} {{Use Indian English|date=January 2018}} {{refimprove|date=January 2017}}{{Anchor|Kanhaiya table of contents}} The '''Kanhaiya''' '''Misl''' was one of the twelve misls of the [[Sikh Confederacy]]. It had been founded by {{Anchor|Misaldar Jai Singh Kanhaiya a Sandhu Jat}} [[Sandhu]] [[Jat people|Jats]].<ref name=SH4>{{Cite web |url=http://www.sikh-history.com/sikhhist/events/m-kanhaiya.html |title=Kanhaiya misl of Sandhu Jats |access-date=24 April 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180815162834/http://www.sikh-history.com/sikhhist/events/m-kanhaiya.html |archive-date=15 August 2018 |url-status=dead }}{{Verification needed|date=October 2024}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Dhir |first=Krishna S. |url=https://books.google.com.mx/books?id=jVx6EAAAQBAJ&pg=PA536&dq=Kanhaiya+misl/?under+Sandhu%25Jats#_.&hl=en&newbks=1&newbks_redir=0&source=gb_mobile_search&ovdme=1&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwjPsfuK6vyIAxVXMtAFHTvEOLYQ6AF6BAgHEAM |title=The Wonder That Is Urdu |date=2022-01-01 |publisher=Motilal Banarsidass |isbn=978-81-208-4301-1 |page=536 |language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Singh |first=Harbans |url=https://books.google.com.mx/books?id=AUhOAQAAMAAJ&q=Kanhaiya?misl/&under+Sandhu%25Jats#_.&dq=Kanhaiya?misl/&under+Sandhu%25Jats#_.&hl=en&newbks=1&newbks_redir=0&source=gb_mobile_search&ovdme=1&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwjW6aq16vyIAxUhMdAFHSgiOpEQ6AF6BAgOEAM |title=The Encyclopaedia of Sikhism: E-L |date=1992 |publisher=Punjabi University |isbn=978-81-7380-204-1 |page=623 |language=en |quote=Kanhaiya clan or chiefship, commonly designated mist, was a Sandhü Jay of the village of Kähnä, 21 km southwest of Lahore on the road to Firozpur. He had an humble origin, his father Khushäl (Singh)...}}</ref> {{Misls}} {{TOC Right}}
== History ==
{{See also|Sikh Confederacy}} {{Anchor|Early Phase of emergence}} ===Early History=== [[Sikh Confederacy|Amar Singh Kingra]] led a band of around 100 Sikh youths, with '''Jai Singh''', a Sandhu Jat from <u>Kanha Kachha</u> village, 21 kilometers east of [[Lahore, Pakistan|Lahore ]], serving as his trusted deputy. Jai Singh's father, Khushhal Singh, made a living selling grass and wood in Lahore, but Jai Singh yearned for more, inspired by the daring exploits of the Sikhs. He took the sacred vows of Sikhism, known as pahul, from Nawab Kapur Singh and joined Amar Singh Kingra's band<ref>{{cite book|title=The Sikhs Commonwealth or Rise and Fall of the Sikh Misls |author=Hari Ram Gupta|date=October 2001 |isbn=81-215-0165-2|publisher=Munshilal Manoharlal Pvt.Ltd}}{{Cn|date=October 2024}}</ref>
===Foundation (1748-1812)===
[[Jai Singh Kanhaiya|Jai Singh]] nickname, "''Kanha''" or "''Kanhiya''", stemmed from his village's name, his handsome appearance, reminiscent of Krishna Kanhiya, and his quick reflexes. Under this name, he became the leader of the band, renowned for his bravery and daring. In January 1754, Jai Singh and [[Charat Singh|Charat Singh Sukarchakia]] disguised themselves as Muslims troops and entered Lahore through the Shah Alami Gate, plundering wealthy merchants and jewelers near the Begams' palaces, Parimahal and Rangmahal .<ref name="Singha, Bhagata 1993">Singha, Bhagata (1993). A History of the Sikh Misals. Patiala, India:Publication Bureau, Punjabi University.</ref> === Succession of Jai Singh === Eventually same year, [[Jai Singh Kanhaiya|Jai Singh's]] brother, '''Jhanda Singh''', fell in battle against Nidhan Singh Randhawa at [[Rawalakot|Raval Kot]]. Jai Singh took Jhanda Singh's widow, Desan, as his wife, and in 1759, she gave birth to [[Gurbaksh Singh Kanhaiya]]. Gurbakhsh Singh's first marriage was to [[Nabha State|Hamir Singh of Nabha's]] daughter, followed by a marriage at age nine to Sada Kaur, daughter of Dasaundha Singh of Ankolwala, although some sources suggest [[Sada Kaur]] was Bhuma Singh Bhangi's daughter.<ref>{{cite book|title=The Sikhs Commonwealth or Rise and Fall of the Sikh Misls |author=Hari Ram Gupta|date=October 2001 |isbn=81-215-0165-2|publisher=Munshilal Manoharlal Pvt.Ltd}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Sheikh |first=Majid |date=2015-06-28 |title=HARKING BACK: Amazing genius of Gujjar Singh and his Lahore 'qila' |url=http://www.dawn.com/news/1190931 |access-date=2023-02-04 |website=DAWN.COM |language=en}}</ref> == Gallery == <gallery> File:Painting of possibly Amar Singh Kingra with attendant, mid-late eighteenth century.jpg|Painting of possibly Amar Singh Kingra with attendant, mid-late eighteenth century File:Painting of Jai Singh Kanhaiya receiving Raja Raj Singh and other hill princes with canopy overhead, ca.1774.jpg|Painting of [[Jai Singh Kanhaiya]] receiving Raja Raj Singh and other hill princes with canopy overhead, ca.1774 File:Miniature painting of Gurbaksh Singh Kanhaiya with a fly-whisk attendant. Family atelier of Purkhu of Kangra, ca.1785.jpg|Miniature painting of [[Gurbaksh Singh Kanhaiya]] with a fly-whisk attendant. Family atelier of Purkhu of Kangra, ca.1785 </gallery> == References == Line 22 ⟶ 36: {{Sikh Empire}} [[Category:Misls|Kanhaiya Confederacy]] [[Category:Social groups of Punjab, India]] [[Category:
[[Category:Princely states of Punjab]] [[Category:History of Lahore]]
{{Sikhism-stub}} | |||