Windows 8: Difference between revisions - Wikipedia
 Article Images
Article Images
Content deleted Content added
ViperSnake151 108,038 edits |
|||
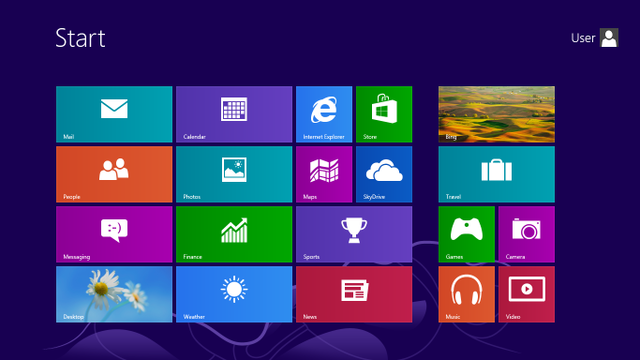
Line 30: }} {{Windows 8}} '''Windows 8''' is a [[personal computer]] [[operating system]] developed by [[Microsoft]] as part of Windows 8 introduced major changes to the operating system's platform and [[graphical user interface|user interface]] to improve its user experience on devices such as [[tablet computer|tablets]], where Windows was now competing with [[mobile operating system]]s such as [[Android (operating system)|Android]] and [[iOS]].<ref name=asd-win8ad/> In particular, these changes included a touch-optimized [[Windows shell]] based on Microsoft's [[Metro (design language)|"Metro"]] [[design language]], the [[Start screen]] (which displays programs and dynamically updated content on a grid of tiles), a new platform for developing [[Mobile app|apps]] with an emphasis on [[touchscreen]] input, integration with online services (including the ability to sync apps and settings between devices), and [[Windows Store]], an online store for downloading and purchasing new software. Windows 8 added support for new and emerging technologies such as [[USB 3.0]], [[Advanced Format]] hard drives, [[near field communication]]s, and [[cloud computing]]. Additional security features were introduced, such as built-in [[antivirus software]], integration with [[Microsoft SmartScreen]] [[Anti-phishing software|phishing filtering]] service and support for [[UEFI Secure Boot]] on supported devices with [[Unified Extensible Firmware Interface|UEFI firmware]], to prevent [[malware]] from infecting the boot process. | |||