Cape Town International Airport
Contributors to Wikimedia projects
 Article Images
Article Images
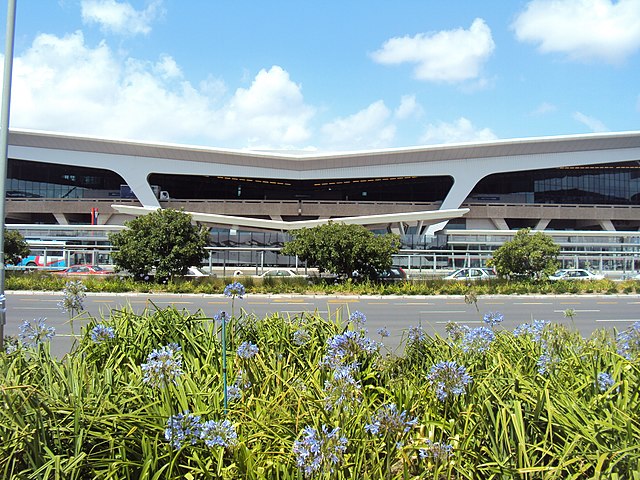
Cape Town International Airport (IATA: CPT, ICAO: FACT) is the primary international airport serving the city of Cape Town, and is the second-busiest airport in South Africa and fifth-busiest in Africa. Located approximately 20 kilometres (12 mi) from the city center, the airport was opened in 1954 to replace Cape Town's previous airport, Wingfield Aerodrome. Cape Town International Airport is the only airport in the Cape Town metropolitan area that offers scheduled passenger services. The airport has domestic and international terminals, linked by a common central terminal.
Cape Town International Airport Kaapstad Internasionale Lughawe (Afrikaans) | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||||||
| Owner/Operator | Airports Company South Africa | ||||||||||||||
| Serves | City of Cape Town | ||||||||||||||
| Location | Matroosfontein, Western Cape, South Africa | ||||||||||||||
| Opened | 1954; 70 years ago | ||||||||||||||
| Hub for | |||||||||||||||
| Focus city for | South African Airways | ||||||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 46 m / 151 ft | ||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 33°58′10″S 018°35′50″E / 33.96944°S 18.59722°E | ||||||||||||||
| Website | airports.co.za | ||||||||||||||
| Map | |||||||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| Statistics (April–March 2024) | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
Source: Passenger and Aircraft Statistics[1] | |||||||||||||||
The airport has direct flights from South Africa's other two main urban areas, Johannesburg and Durban, as well as flights to smaller centers in South Africa. Internationally, it has direct flights to several destinations in Africa, the Middle East, Asia, Europe, South America and the United States. The air route between Cape Town and Johannesburg was the world's ninth-busiest air route in 2011 with an estimated 4.5 million passengers.[2]
D.F. Malan Airport was opened in 1954, a year after Jan Smuts Airport (now O. R. Tambo International Airport) on the Witwatersrand, near Johannesburg, opened. The airport replaced Cape Town's previous airport, Wingfield Aerodrome. Originally named after the then South African prime minister, it initially offered two international flights: a direct flight to Britain and a second flight to Britain via Johannesburg.[3]
With the fall of apartheid in the early 1990s, ownership of the airport was transferred from the state to the newly formed Airports Company South Africa,[4] and the airport was renamed to the politically neutral Cape Town International Airport.[5] South African Airways launched a route to Miami in December 1992.[6] In January 2000, the carrier replaced it with a flight to Atlanta, whose outbound leg from Cape Town included a stop in Fort Lauderdale.[7]
The first years of the twenty-first century saw tremendous growth at the airport; from handling 6.2 million passengers per annum in 2004–05, the airport peaked at 8.4 million passengers per annum in 2007–08 before falling back to 7.8 million in 2008–09.[citation needed] In June 2008, Delta Air Lines started a flight to New York via Dakar. It used a Boeing 767 on the route.[8][9] Delta began flying to Atlanta instead the following June. The company terminated the route in September 2009.[10][11] In December 2011, Malaysia Airlines discontinued its service to Buenos Aires.[12][13]
In 2016, the airport saw a 29% increase in international arrivals; 2016 also saw the airport handle 10 million passengers per annum.[citation needed][14] United Airlines commenced seasonal flights to Newark on a Boeing 787 in December 2019.[15] The route became year-round in 2022.[16] In October 2023, South African Airways inaugurated a link to São Paulo.[17]
On 16 April 2018, it was reported in the Cape Times that the Minister of Transport, Bonginkosi Nzimande, had directed ACSA on 22 March 2018 to change the name of Cape Town International Airport to Nelson Mandela International Airport.[18] The name change was discussed and as yet no name change had been published in the Government Gazette.[19]
On 5 March 2019, the EFF filed a motion in Parliament calling for the renaming of Cape Town International Airport after anti-apartheid icon Winnie Madikizela-Mandela. While members of the Khoi community pushed for the airport to be named after the !Uriǁ'aeǀona translator and cultural icon Krotoa.[20] One of the arguments of the opposition was that Parliament is not constitutionally empowered to resolve any name change and that it was the responsibility of the South African Geographical Names Council (SAGNC) to deal with name changes. The motion was not successful.[21]
Until a name change has been published in the Government Gazette, it remains Cape Town International Airport. In February 2021, the Cape Times reported that the proposed name change of the airport had been "quietly ditched".[22]
In preparation for the 2010 FIFA World Cup, Cape Town International Airport was extensively expanded and renovated. The main focus was the development of a Central Terminal Building at a cost of R1.6 billion,[23] which linked the formerly separate domestic and international terminals and provided a common check-in area.[24] The departures level of the Central Terminal opened in November 2009, with the entire building opened in April 2010.[23]
Apart from the now-completed 2010 expansion project, it had been proposed that a second runway for large aircraft be constructed at the airport, to be completed by 2015. However, this second runway has not been constructed. In May 2015, Airports Company South Africa announced a R7.7 billion expansion for the airport. The expansion includes the upgrades of the Domestic & International terminals. The expansion has been postponed indefinitely due to the drop in passenger numbers due to the global COVID-19 pandemic from 2020.[25]
The airport has two terminals linked together by one central terminal.
The terminal building has a split-level design, with departures located on the upper floors and arrivals in the lower floors; an elevated roadway system provides vehicular access to both departures and arrivals levels.[24] All check-in takes place within the Central Terminal Building, which contains 120 check-in desks and 20 self-service kiosks.[24] Passengers then pass through a consolidated security screening area before dividing. Passengers flying internationally head to the northern part of the airport which is the international terminal, and passengers flying to other parts of South Africa head to the southern part of the airport to the domestic terminal.
The terminal has 10 air bridges, evenly split between domestic and international usage. Sections of lower levels of the domestic and international terminals are used for transporting passengers via bus to and from remotely parked aircraft.[24]
Arriving passengers collect luggage in the old sections of their respective terminals, before proceeding through new passageways to the new Central Terminal Building.[23] The terminal contains an automated baggage handling system, capable of handling 30,000 bags per hour.[24]
Retail outlets are located on the lower (arrivals) level of the terminal at landside, as well as airside at the departure gates. Retail outlets are diverse, including foreign exchange services, bookstores, clothing retailers, grocery stores, souvenir outlets and duty-free in international departures. Restaurants within the terminal building are located on the upper (3rd) level above the departures level, which includes what is purported to be the largest Spur restaurant on the African continent, at 1,080 m2 (11,600 sq ft).[24] The restaurant level overlooks the airside of the terminal, where a glass curtain wall separates the patrons from the planes three stories below. On the 4th floor is where the airport's lounges are situated. The Bidvest, as well as South African Airways lounges, can be found here.
International Terminal
The international terminal is located on the northern side of the airport. Customs and Immigration facilities, lounges, duty-free shops, restaurants, prayer rooms, conference rooms, airline offices, and chapels are located in the terminal.
Located on the southern side of the airport, it has the same facilities as the international terminal, with the exception of Immigration facilities.
There are two hotels located within the airport precinct: Hotel Verde, a four-star hotel owned by Bon Hotels and ranked as "Africa's greenest hotel",[26] and the other being Road Lodge, a budget hotel owned by the City Lodge hotel chain group. An ExecuJet facility is located near the southern end of the main runway and caters for business jets.
Airlines and destinations
- Notes
- ^a Kenya Airways flights to Nairobi operate via Victoria Falls and Livingstone.
- ^b Flights to and from Kigali have a stopover in Harare. The airline has full traffic rights to transport passengers between Harare and Cape Town.
- ^c This flight operates via Johannesburg. However, this carrier does not have rights to transport passengers solely between Cape Town and Johannesburg.
- ^d Some Delta Air Lines flights from Atlanta to Cape Town operate via Johannesburg. However, all flights from Cape Town to Atlanta are nonstop.
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| BidAir Cargo[57] | Johannesburg–Lanseria, Johannesburg–O. R. Tambo, Port Elizabeth |
| Fiscal year | International | Regional | Domestic | Unscheduled | Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Passenger movements | % Change | Passenger movements | % Change | Passenger movements | % Change | Passenger movements | % Change | Passenger movements | % Change | |
| 2004–05 | 1,176,958 | no data | 126,837 | no data | 4,895,048 | no data | 16,060 | no data | 6,214,903 | no data |
| 2005–06 | 1,167,661 | 0.8% | 149,489 | 17.9% | 5,503,690 | 12.4% | 13,333 | 17.0% | 6,834,173 | 10.0% |
| 2006–07 | 1,246,016 | 6.7% | 147,885 | 1.1% | 6,107,405 | 11.0% | 17,237 | 29.3% | 7,518,543 | 10.0% |
| 2007–08 | 1,309,822 | 5.1% | 145,858 | 1.4% | 6,950,061 | 13.8% | 20,877 | 21.1% | 8,426,618 | 12.1% |
| 2008–09 | 1,378,160 | 5.2% | 138,000 | 5.4% | 6,283,132 | 9.6% | 13,878 | 33.5% | 7,813,170 | 7.3% |
| 2009–10 | 1,284,990 | 6.8% | 122,584 | 11.2% | 6,391,079 | 1.7% | 11,416 | 17.7% | 7,810,069 | 0.0% |
| 2010–11 | 1,261,024 | 1.9% | 122,609 | 0.0% | 6,781,143 | 6.1% | 35,771 | 213% | 8,200,547 | 5.0% |
| 2011–12 | 1,400,487 | 11.1% | 133,280 | 8.7% | 7,028,669 | 3.7% | 13,902 | 157% | 8,576,338 | 4.6% |
| 2012–13 | 1,325,481 | 5.4% | 144,148 | 8.2% | 6,951,577 | 1.1% | 13,593 | 2.2% | 8,434,799 | 1.7% |
| 2013–14 | 1,355,524 | 2.3% | 143,356 | 0.7% | 6,879,919 | 1.0% | 14,190 | 4.4% | 8,392,989 | 0.5% |
| 2014–15 | 1,452,360 | 7.1% | 150,602 | 5.1% | 7,142,907 | 3.9% | 10,003 | 41.9% | 8,755,872 | 4.3% |
| 2015–16 | 1,564,464 | 7.7% | 179,775 | 19.4% | 7,902,362 | 10.6% | 12,988 | 29.8% | 9,659,589 | 10.3% |
| 2016–17 | 1,934,641 | 23.7% | 197,437 | 9.8% | 8,067,516 | 2.1% | 11,796 | 9.2% | 10,211,390 | 5.7% |
| 2017–18 | 2,243,367 | 16% | 208,903 | 5.8% | 8,286,618 | 2.7% | 13,358 | 13.2% | 10,752,246 | 5.3% |
| 2018–19 | 2,406,594 | 7.3% | 195,617 | 6.4% | 8,209,610 | 0.1% | 11,916 | 10.8% | 10,823,737 | 0.1% |
| 2019–20 | 2,356,225 | 2.1% | 183,999 | 5.9% | 8,137,246 | 0.9% | 11,328 | 4.9% | 10,688,798 | 1.2% |
| 2020–21 | 156,433 [a] | 93.4% | 15,484 | 91.6% | 2,181,670 | 73.2% | 32,534 | 187.2% | 2,386,121 | 77.7% |
| 2021-22 | 751,278 | 131% | 80,384 | 135% | 4,853,699 | 76% | 15,450 | 53% | 5,700,811 | 82% |
| 2022-23 | 2,174,073 | 189% | 149,299 | 86% | 6,062,223 | 25% | 22,156 | 43% | 8,407,751 | 47% |
| 2023-24 | 2 754 405 | 23.6% | 169 961 | 12.9% | 7 093 292 | 15.7% | 16 694 | 12.1% | 10 034 352 | 17.6% |
| Fiscal year | International | Regional | Domestic | Unscheduled | Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aircraft movements | % Change | Aircraft movements | % Change | Aircraft movements | % Change | Aircraft movements | % Change | Aircraft movements | % Change | |
| 2004–05 | 4,355 | no data | 4,242 | no data | 56,810 | no data | 27,154 | no data | 92,561 | no data |
| 2005–06 | 4,296 | 1.4% | 4,169 | 1.7% | 58,099 | 2.3% | 22,326 | 17.8% | 88,890 | 4.0% |
| 2006–07 | 4,623 | 7.6% | 3,698 | 11.3% | 60,470 | 4.1% | 22,602 | 1.2% | 91,393 | 2.8% |
| 2007–08 | 5,019 | 8.6% | 3,420 | 7.5% | 69,819 | 15.5% | 24,027 | 6.3% | 102,285 | 11.9% |
| 2008–09 | 5,638 | 12.3% | 3,340 | 2.3% | 65,623 | 6.0% | 21,042 | 12.4% | 95,643 | 6.5% |
| 2009–10 | 4,884 | 13.4% | 3,296 | 1.3% | 65,020 | 0.9% | 19,379 | 7.9% | 92,579 | 3.2% |
| 2010–11 | 4,868 | 0.3% | 3,137 | 4.8% | 66,587 | 2.4% | 19,031 | 1.8% | 93,623 | 1.1% |
| 2012–13 | 4,906 | 0.8% | 3,557 | 4.8% | 62,065 | 6.7% | 18,545 | 1.8% | 89,073 | 4.9% |
| 2013–14 | 4,961 | 1.1% | 2,855 | 4.8% | 60,665 | 2.3% | 20,092 | 1.8% | 88,573 | 0.6% |
| 2014–15 | 5,091 | 2.6% | 3,135 | 4.8% | 64,269 | 5.9% | 18,651 | 1.8% | 91,146 | 2.9% |
| 2015–16 | 5,568 | 9.4% | 4,783 | 4.8% | 70,731 | 10% | 19,139 | 1.8% | 100,221 | 10% |
| 2016–17 | 7,121 | 27.9% | 5,048 | 4.8% | 71,081 | 0.5% | 16,087 | 1.8% | 99,337 | 0.9% |
| 2017–18 | 9,206 | 29.3% | 5,048 | 4.8% | 72,110 | 1.4% | 16,252 | 1.8% | 103,001 | 3.7% |
| 2018–19 | 10,490 | 13.9% | 4,950 | 1.9% | 67,328 | 6.6% | 15,898 | 2.2% | 98,666 | 4.2% |
| 2019–20 | 10,154 | 3.2% | 4,206 | 15.0% | 65,372 | 2.9% | 10,447 | 34.3% | 90,179 | 8.6% |
| 2020–21 | 1,369 | 86.5% | 644 | 84.7% | 20,287 | 69.0% | 16,618 | 59.1% | 38,918 | 56.8% |
| 2021–22 | 5,202 | 280.0% | 2,607 | 304.8% | 45,149 | 122.6% | 14,738 | 11.3% | 67,696 | 73.9% |
| 2022–23 | 10,913 | 109.8% | 3,704 | 42.1% | 52,087 | 15.4% | 23,576 | 60.0% | 90,280 | 33.4% |
| 2023–24 | 14,184 | 30.0% | 3,993 | 7.8% | 61,482 | 18.0% | 19,479 | 17.4% | 99,138 | 9.8% |
Cape Town International Airport is approximately 20 kilometres (12 mi) from the city centre and is accessible from the N2 freeway, with Airport Approach Road providing a direct link between the N2 (at exit 16) and the airport. The airport can also be indirectly accessed from the R300 freeway via the M12, M10 and M22.
The airport provides approximately 1,424 parking spaces in the general parking area, and 1,748 parking bays in the multi-storey car park located near the domestic terminal.[60] A new car park opened in 2010, which is located near the international terminal and provides an additional 4,000 parking spaces.[61] The airport also offers a valet parking service.[60]
Transport to and from the airport is provided by metered taxis, e-hailing services (such as Uber and Bolt) and various private shuttle companies.
There is no direct rail access to Cape Town International Airport. The Passenger Rail Agency of South Africa has proposed a 4 km (2.5 mi) rail link between the airport and Cape Town's existing suburban rail network.
- ^ Reductions due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- ^ "Cape Town International Airport Passenger Statistics". Airports Company South Africa.
- ^ The Economist, Online (14 May 2012). "Top Flights". The Economist. Archived from the original on 5 June 2012. Retrieved 6 June 2012.
- ^ Bickford-Smith, Vivian; E. Van Heyningen; Nigel Worden (1999). Cape Town in the twentieth century: an illustrated social history. Cape Town: New Africa Books. p. 120. ISBN 978-0-86486-384-3.
- ^ "ACSA – History". Airports Company South Africa. Archived from the original on 20 July 2011. Retrieved 28 December 2009.
- ^ "Cape Town Airport (CPT) Information – Airports Guide to Cape Town". airports-guides.com. Archived from the original on 28 March 2013. Retrieved 28 December 2009.
- ^ "Trip tips: Bulletin board". The Orlando Sentinel. 13 December 1992. p. H-1. Retrieved 4 December 2021.
- ^ Stieghorst, Tom (27 January 2000). "S. African flights arriving soon". South Florida Sun Sentinel. pp. 1D, 2D.
- ^ Laun, Chelsea (5 June 2008). "Delta launches direct flights between city and New York". Cape Times. ProQuest 430682700.
- ^ Mackenzie, Jacqueline (26 September 2007). "Delta Air adds new SA route". News24. Retrieved 23 July 2023.
- ^ "Delta to Offer Customers Service to More Unique International Destinations in 2009" (Press release). Delta Air Lines. 12 November 2008. Retrieved 23 July 2023.
- ^ Yamanouchi, Kelly (20 June 2009). "Delta trims overseas routes, including Cape Town flights". The Atlanta Journal-Constitution. Retrieved 23 July 2023.
- ^ "Malaysia Airlines pulls out of SA". Independent Online. 11 January 2012. Retrieved 4 December 2021.
- ^ "New oneworld member Malaysia Airlines seeks to finally turn the corner in 2013 but challenges remain". CAPA - Centre for Aviation. 27 December 2012. Retrieved 4 December 2021.
- ^ Jooste, Bronwynne (10 January 2017). "Cape Town International welcomes 10 millionth passenger". www.westerncape.gov.za. Retrieved 13 June 2024.
- ^ Githahu, Mwangi (17 December 2019). "Cape Town welcomes inaugural United Airlines flight". Independent Online. Retrieved 4 December 2021.
- ^ "United to Become First Airline to Fly Nonstop Between Washington D.C. and Cape Town" (Press release). United Airlines. 28 July 2022. Retrieved 23 July 2023.
- ^ Silk, Robert (30 June 2023). "South African Airways to resume transatlantic flying". Travel Weekly. Retrieved 23 July 2023.
- ^ Villette, Francesca (16 April 2018). "Cape Town International Airport IS to be renamed". iol.co.za. Cape Times. Archived from the original on 14 February 2019. Retrieved 13 February 2019.
- ^ "Government Gazette online (search)". Green Gazette. 13 February 2019. Archived from the original on 14 February 2019. Retrieved 13 February 2019.
- ^ Solwandle, Nomawethu (18 September 2018). "Khoisan groups want Cape Town Airport named after Krotoa". SABC News. Archived from the original on 14 December 2018. Retrieved 16 March 2021.
- ^ "ANC shoots down EFF plan to rename Cape Town airport after Mama Winnie". Archived from the original on 6 March 2019. Retrieved 6 March 2019.
- ^ Villette, Francesca (26 February 2021). "Cape Town airport name change ditched". www.iol.co.za. Archived from the original on 26 February 2021. Retrieved 16 March 2021.
- ^ a b c Nicholson, Zara (8 November 2009). "New terminal hailed as a success". Sunday Argus. IOL. Archived from the original on 24 November 2009. Retrieved 28 December 2009.
- ^ a b c d e f "ACSA – New Developments". Airports Company South Africa. Archived from the original on 20 July 2011. Retrieved 28 December 2009.
- ^ "Covid grounds R7bn Cape Town airport expansion". Independent Online. 10 February 2022. Retrieved 1 June 2022.
- ^ "These are the 10 best airport hotels in the world". The Independent. 2 March 2018. Archived from the original on 12 March 2018.
- ^ a b "Air Botswana Network Expansion From Sep 2024". Aeroroutes. Retrieved 3 September 2024.
- ^ "Air France returns to South African skies". 26 October 2021.
- ^ "New winter route from Air France: Cape Town to Paris". 6 July 2023.
- ^ "AIR MAURITIUS RESUMES CAPE TOWN SEASONAL SERVICE IN NW22". Aeroroutes. 5 August 2022. Retrieved 5 August 2022.
- ^ "Airlink to connect Cape Town with Gaborone". 5 August 2024.
- ^ "Airlink to introduce flights between Cape Town and Harare from Jan 18". 18 December 2020.
- ^ "Airlink to connect Cape Town and Maputo with direct flights | Flyairlink".
- ^ Smith, Carin. "Airlink jumps in with new West Coast route while Air Namibia heads for liquidation". Business. Retrieved 24 December 2022.
- ^ "AeroRoutes". 26 July 2024.
- ^ Schedules British Airways
- ^ "FlyCemAir launches East London to Cape Town flights".
- ^ "CemAir Adds Cape Town - Kimberely Service From Mid-Feb 2023". AeroRoutes. 3 February 2023. Retrieved 3 February 2023.
- ^ "CemAir / Scheduled flights in South Africa". www.flycemair.co.za. Retrieved 24 December 2022.
- ^ "Delta launches new route between Cape Town and Atlanta". Iol. 2 December 2022. Retrieved 3 December 2022.
- ^ "Emirates resumes flights to South Africa, Mauritius and Zimbabwe". 24 September 2020.
- ^ "SA to Swaziland: Eswatini Air to launch flights in South Africa this March". 3 March 2023.
- ^ "New SA route alert: FlySafair launches flights between Bloemfontein and Cape Town".
- ^ "Safair Plans Cape Town – Nelspruit Service From April 2024". Aeroroutes. Retrieved 22 November 2023.
- ^ "FlySafair to launch Windhoek flights". 2 September 2024.
- ^ "Airlines increasing frequencies to Cape Town". 21 November 2023.
- ^ "LIFT | SA's Flexible Airline".
- ^ "Mango welcomes Court Decision to place it under business rescue" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 June 2023. Retrieved 16 August 2021.
- ^ "Norse Atlantic Airways Introduces New Route Between London Gatwick and Cape Town". 8 April 2024.
- ^ Philipot, Lorne (12 May 2021). "Cape Town back on Singapore Airlines' route network". The South African. Blue Sky Publications.
- ^ Jim Liu. "Singapore Airlines NW22 Passenger Operations as of 25 July 2022". Aeroroutes.
- ^ "SAA takes off on September 23 with these routes".
- ^ "South African anuncia retorno ao Brasil com rota inédita para a Cidade do Cabo". Aeroin (in Portuguese). 29 June 2023. Retrieved 29 June 2023.
- ^ "United and Delta Launch Nonstop Services to Cape Town". August 2022.
- ^ "United to Become First Airline to Fly Nonstop Between Washington D.C. and Cape Town" (Press release). Chicago: United Airlines. 28 July 2022.
- ^ Ltd, Jacobs Media Group. "Virgin Atlantic outlines winter sun schedule". Travel Weekly. Retrieved 24 December 2022.
- ^ bidaircargo.com - Network retrieved 13 January 2021
- ^ "ACSA – Cape Town Passenger Statistics". Airports Company South Africa.
- ^ "ACSA – Cape Town Aircraft Statistics". Airports Company South Africa. Retrieved 4 September 2024.
- ^ a b "ACSA – Cape Town – Maps and parking". Airports Company South Africa. Archived from the original on 13 November 2008. Retrieved 28 December 2009.
- ^ "More parking comes online at Cape Town International Airport". Airports Company South Africa. 10 December 2009. Archived from the original on 20 July 2011. Retrieved 28 December 2009.
Media related to Cape Town International Airport at Wikimedia Commons