Portal:Socialism - Wikipedia

Socialism is an economic and political philosophy encompassing diverse economic and social systems characterised by social ownership of the means of production, as opposed to private ownership. It describes the economic, political, and social theories and movements associated with the implementation of such systems. Social ownership can take various forms, including public, community, collective, cooperative, or employee. As one of the main ideologies on the political spectrum, socialism is considered the standard left wing ideology in most countries of the world. Types of socialism vary based on the role of markets and planning in resource allocation, and the structure of management in organizations.
The socialist political movement includes political philosophies that originated in the revolutionary movements of the mid-to-late 18th century and out of concern for the social problems that socialists associated with capitalism. By the late 19th century, after the work of Karl Marx and his collaborator Friedrich Engels, socialism had come to signify anti-capitalism and advocacy for a post-capitalist system based on some form of social ownership of the means of production. By the early 1920s, communism and social democracy had become the two dominant political tendencies within the international socialist movement, with socialism itself becoming the most influential secular movement of the 20th century. Many socialists also adopted the causes of other social movements, such as feminism, environmentalism, and progressivism. (Full article...)
Selected article
The International Union of Socialist Youth (IUSY) (founded in 1907), is a global political youth organisation, representing socialist and organised labour youth organisations. IUSY's work centers around supporting its member organizations, publishing bulletins, and organizing international annual youth gatherings.
Founded in 1907 as the youth wing of the Second International under the name Socialist Youth International, IUSY now represents 134 member organisations in over 80 countries. IUSY is an international youth NGO with UN ECOSOC consultative status, which it gained in 1993.
Selected biography - show another
Hugo Rafael Chávez Frías[a] (Spanish pronunciation: [ˈuɣo rafaˈel ˈtʃaβes ˈfɾi.as] ⓘ; 28 July 1954 – 5 March 2013) was a Venezuelan politician and military officer who served as the 52nd president of Venezuela from 1999 until his death in 2013, except for a brief period of forty-seven hours in 2002. Chávez was also leader of the Fifth Republic Movement political party from its foundation in 1997 until 2007, when it merged with several other parties to form the United Socialist Party of Venezuela (PSUV), which he led until 2012.
Born into a middle-class family in Sabaneta, Barinas, Chávez became a career military officer. After becoming dissatisfied with the Venezuelan political system based on the Puntofijo Pact, he founded the clandestine Revolutionary Bolivarian Movement-200 (MBR-200) in the early 1980s. Chávez led the MBR-200 in its unsuccessful coup d'état against the Democratic Action government of President Carlos Andrés Pérez in 1992, for which he was imprisoned. Pardoned from prison two years later, he founded the Fifth Republic Movement political party, and then receiving 56.2% of the vote, was elected president of Venezuela in 1998. He was re-elected in 2000 with 59.8% of the vote and again in 2006 with 62.8% of the vote. After winning his fourth term as president in the October 2012 presidential election with 55.1% of the vote, he was to be sworn in on 10 January 2013. However, the inauguration was cancelled due to his cancer treatment, and on 5 March at age 58, he died in Caracas. (Full article...)
General images
The following are images from various socialism-related articles on Wikipedia.
-
The first anarchist journal to use the term libertarian was Le Libertaire, Journal du Mouvement Social, published in New York City between 1858 and 1861 by French libertarian communist Joseph Déjacque, the first recorded person to describe himself as libertarian. (from Socialism)
-
Albert Einstein advocated for a socialist planned economy with his 1949 article "Why Socialism?" (from Socialism)
-
Mao Zedong in 1959 (from History of socialism)
-
Statue of Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels in Alexanderplatz, Berlin (from History of socialism)
-
Russian anarchist Mikhail Bakunin opposed the Marxist aim of dictatorship of the proletariat in favour of universal rebellion and allied himself with the federalists in the First International before his expulsion by the Marxists (from History of socialism)
-
New Harmony, a utopian attempt as proposed by Robert Owen (from Socialism)
-
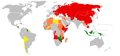
World Map of Socialist countries in 1985 (from History of socialism)
-
Pierre-Joseph Proudhon, main theorist of mutualism and influential French socialist thinker (from Socialism)
-
Edward Carpenter, philosopher and activist who was instrumental in the foundation of the Fabian Society and the Labour Party as well as in the early LGBTI western movements (from Socialism)
-
Kwame Nkrumah, the first president of Ghana and theorist of African socialism, on a Soviet Union commemorative postage stamp (from History of socialism)
-
Project Cybersyn was an early form of computational economic planning (from Socialism)
-
Barricades Boulevard Voltaire, Paris during the uprising known as the Paris Commune (from History of socialism)
-
Claude Henri de Rouvroy, comte de Saint-Simon, early French socialist (from Socialism)
-
R. H. Tawney, founder of ethical socialism (from Socialism)
-
Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist Vladimir Lenin in 1920 (from Socialism)
-
Noam Chomsky, an American libertarian socialist (from History of socialism)
-
Claude Henri de Rouvroy, Comte de Saint-Simon, founder of French socialism (from History of socialism)
-
Alexis Tsipras, socialist Prime Minister of Greece who led the Coalition of the Radical Left (SYRIZA) through a victory in the January 2015 Greek legislative election (from History of socialism)
-
New Harmony, a utopian attempt as proposed by Robert Owen (from History of socialism)
-
Encounter between Simone de Beauvoir, Jean-Paul Sartre and Che Guevara in Cuba, three radical icons of the 1960s (from History of socialism)
-
Arabic letters "Lam" and "Alif" reading "Lā" (Arabic for "No!") are a symbol of Islamic Socialism in Turkey. (from Socialism)
-
Socialists in Union Square, New York City on May Day 1912 (from Socialism)
-
Albert Einstein advocated for a socialist planned economy with his 1949 article "Why Socialism?" (from History of socialism)
-
Man, Controller of the Universe produced by Mexican artist Diego Rivera (from Socialism)
-
Socialist feminist Clara Zetkin and Rosa Luxemburg in 1910 (from Socialism)
-
Presidents Fernando Lugo of Paraguay, Evo Morales of Bolivia, Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva of Brazil, Rafael Correa of Ecuador and Hugo Chávez of Venezuela in World Social Forum for Latin America (from History of socialism)
-
The Soviet of Workers' Deputies of St. Petersburg in 1905, Trotsky in the center. The soviets were an early example of a workers council. (from History of socialism)
-
The writings of Karl Marx provided the basis for the development of Marxist political theory and Marxian economics. (from Socialism)
-
The Soviet of Workers' Deputies of St. Petersburg in 1905, Trotsky in the center. The soviets were an early example of a workers council. (from Socialism)
-
Pierre Leroux founder of the Parisian newspaper Le Globe in which the term socialism first appeared (from History of socialism)
-
Mikhail Bakunin speaking to members of the IWA at the Basel Congress in 1869 (from History of socialism)
Did you know (auto-generated) - load new batch

- ... that Julia Dawson's first Clarion Van was named for Scottish socialist Caroline Martyn?
- ... that in 1968, actor Ludovic Antal recited a Romanian nationalist poem in front of tourists from Soviet Moldavia, causing them to flee for their bus for fear of a "provocation"?
- ... that a priest refused to perform the wedding ceremony for Austrian socialist Josef Peskoller and his fiancée Maria Griel on political grounds in 1928?
- ... that by mid-1920, hundreds of German and Austrian communists fought in Red Army units in Turkestan?
- ... that the Eurovision Song Contest 1990, held in Yugoslavia, was the first Eurovision Song Contest to be held in the Balkans or in a socialist state?
- ... that Left Socialist-Revolutionary leader Maria Spiridonova addressed her party's fourth congress in October 1918 by letter as she was in jail?
- ... that although the 1950 Mexican film Un día de vida (pamphlet pictured) bombed with domestic audiences, it became a classic in Yugoslavia?
Topics
Subcategories

Want to find an article related to socialism? Try browsing through any of the main categories below:
Select [►] to view subcategories
Selected quotation
| “ | Marxian morality is likewise of English origin. Marxism reveals in every sentence that the thought processes from which it sprang were theological and not political. Its economic theory is the outgrowth of a fundamental moral attitude, and the materialistic view of history is simply the final chapter of a philosophy with roots in the English Revolution, whose biblical moods have remained dominant in English thought.
That is why Marx’s basic concepts are felt to be moral alternatives. The words "socialism" and "capitalism" are terms for the good and evil of this irreligious religion. The "bourgeois" is the devil, the wage earner is the angel of a new mythology, and one need only sample the vulgar paths of the Communist Manifesto to recognize behind the literary mask the Christianity of the Independents. Social evolution is "the will of God." The "final goal," in an earlier age, was eternal salvation; the "collapse of bourgeois civilization" used to be called the Last Judgment. |
” |
| — Oswald Spengler, "Prussianism And Socialism", 1919 | ||
Participate!
Everyone is welcome to participate in WikiProject Socialism, where editors collaborate to improve all aspects related to socialism on Wikipedia.
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Discover Wikipedia using portals
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).